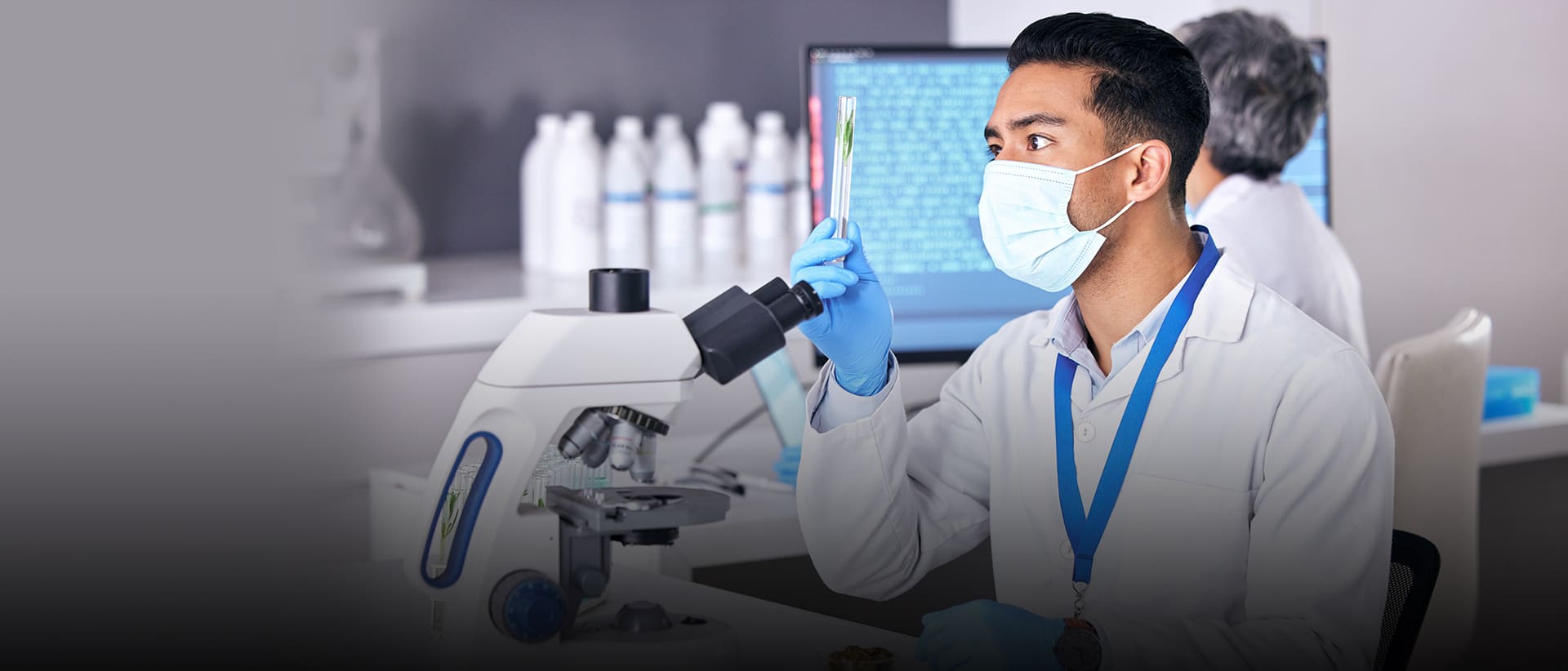
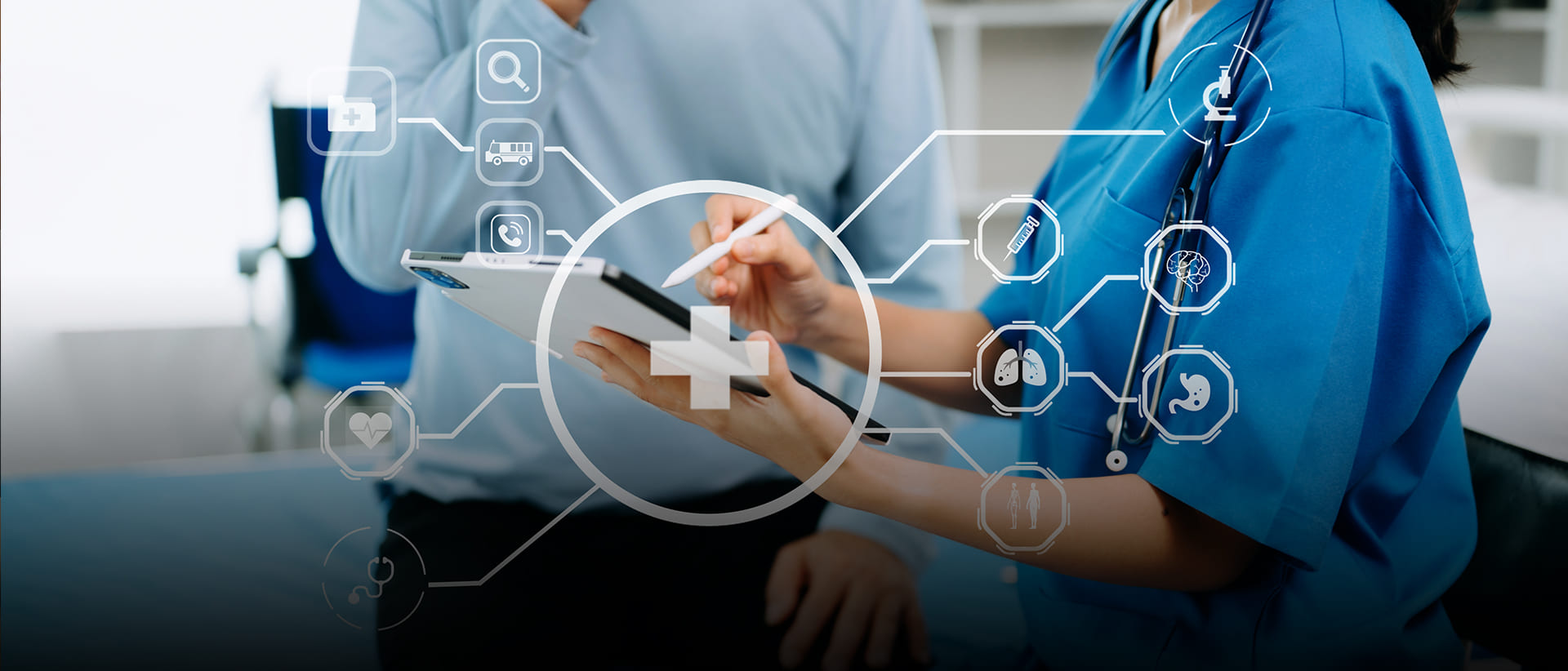
Health Informatics stands at the forefront of revolutionizing healthcare delivery, leveraging cutting-edge technology and data analytics to shape the future of patient care and population health. In an era where healthcare data is exponentially growing, Health Informatics professionals play a pivotal role in harnessing this wealth of information to drive informed decision-making, improve patient outcomes, and enhance healthcare efficiency. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Health Informatics has been instrumental in supporting healthcare systems worldwide. For instance, contact tracing applications and real-time data dashboards have been developed to track the spread of the virus, identify hotspots, and allocate resources effectively. Telehealth platforms have facilitated remote consultations, enabling patients to access medical advice while minimizing the risk of exposure to the virus. Additionally, predictive analytics models have been employed to forecast healthcare demands, helping hospitals and public health authorities anticipate surges in COVID-19 cases and plan accordingly.
In the Master of Science (M.Sc.) program in Health Informatics, students delve into a dynamic curriculum that explores emerging technologies, data-driven decision-making, and innovative healthcare solutions. Through hands-on experiences such as internships, fieldwork, and research projects, students gain practical skills in health data management, information systems development, clinical decision support, and informatics governance. Armed with these skills and insights, graduates emerge as visionary Health Informatics professionals ready to navigate the complexities of the healthcare landscape and drive positive change in patient care and population health outcomes.
2 years
The scope of agriculture has existed from time immemorial, beyond the scope of civilization as a whole thus placing agriculture on a position of great social and economic significance.
Graduate (Any stream)
INDUSTRY LED LEARNING
Gain practical experience utilizing state of the art lab environment to enhance your skill set.


Integration of practical skills:
It allows students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, enhancing their understanding and retention of key concepts. Practical skills enable students to develop problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and decision-making capabilities, which are crucial for success in the field of health informatics


Exposure to advanced technologies:
Exposure to advanced technologies allows them to stay updated with the latest trends and innovations in healthcare technology, preparing them for the rapidly evolving field of health informatics. By working with cutting-edge tools and technologies, students can develop a deeper understanding of how these technologies can be applied to improve healthcare delivery, patient outcomes, and population health.


Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals:
It offers real-world insights into the challenges and complexities of healthcare delivery, helping students understand how their work in informatics can directly impact patient care and healthcare outcomes. Working closely with healthcare professionals allows students to gain a deeper understanding of the specific needs and requirements of healthcare organizations, enabling them to develop informatics solutions that are practical, effective, and aligned with industry standards.


Experiential Learning Opportunities
Experiential learning opportunities enhance the learning experience, prepare students for the demands of the healthcare industry, and help them make meaningful contributions to improving healthcare delivery and outcomes


Access to Mentorship and Networking:
Mentorship provides students with guidance and support from experienced professionals in the field, helping them navigate their academic and professional development. Mentors can offer insights into industry trends, career opportunities, and practical advice on how to succeed in the field of health informatics.


Alignment with Industry standards and Best Practices:
Ensures that students are learning the most up-to-date and relevant information in the field, preparing them for the current demands of the healthcare industry. Alignment with industry standards helps students develop skills and competencies that are directly applicable to their future careers, increasing their employability and effectiveness in the workplace
For an accelerating professional career in the 21st Century along with Core Skills, the learner should evolve through Self-directed Learning, Self-awareness, Multidisciplinary Problem Solving, Practice of Professional Grade, Digital Comfort, Current Social and Global Dynamics, Employability, and Life Skills. MSU offers an opportunity to customize higher education with a range of specialization/electives.
Foundation Core
A range of compulsory basics of multidisciplinary, professional, general nature customised to match the value and vision of MSU for a robust foundation.
Skill Drill (Elective)
A range of compulsory basics of multidisciplinary, professional, general nature customised to match the value and vision of MSU for a robust foundation.
Minor (Elective)
A range of compulsory basics of multidisciplinary, professional, general nature customised to match the value and vision of MSU for a robust foundation.
Major (Elective)
A range of compulsory basics of multidisciplinary, professional, general nature customised to match the value and vision of MSU for a robust foundation.
Industry Practice
A range of compulsory basics of multidisciplinary, professional, general nature customised to match the value and vision of MSU for a robust foundation.
Capstone Project
A range of compulsory basics of multidisciplinary, professional, general nature customised to match the value and vision of MSU for a robust foundation.
Program Outcomes
PSO 1:
Master health data collection, storage, and analysis techniques, ensuring data integrity and security.
PSO 2:
Design and implement advanced health information systems to optimize healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes.
PSO 3:
Develop expertise in designing clinical decision support systems to provide healthcare professionals with actionable insights for patient care.
PSO 4:
Understand the regulatory and ethical considerations in health informatics, enabling them to develop governance frameworks that protect patient confidentiality.
PSO 5:
Cultivate communication and collaboration skills to work effectively with healthcare professionals, IT specialists, and policymakers to address healthcare challenges and promote health equity.
PSO 6:
Critically evaluate and apply current research findings and evidence-based practices in public health interventions, ensuring that their strategies are grounded in scientific rigor and effectiveness.
PSO 1:
Demonstrate the capability for complex problem-solving
PSO 2:
Demonstrate the capability for critical thinking
PSO 3:
Demonstrate the ability for creativity
PSO 4:
Demonstrate the skills that enable them to communicate effectively
PSO 5:
Demonstrate the capability for analytical reasoning/thinking
PSO 6:
Demonstrate the ability for coordinating and collaborating with others
PSO 7:
Demonstrate the capability for leadership readiness
PSO 8:
Demonstrate ‘learning how to learn" skills
PSO 9:
Demonstrate the capability for digital and technological skills
PSO 10:
Demonstrate multicultural competence and inclusive spirit
PSO 11:
Demonstrate the acquisition of knowledge and attitude that are required for value inculcation
PSO 12:
Demonstrate the ability for autonomy, responsibility, and accountability
PSO 13:
Demonstrate the acquisition of and ability to apply the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values required to take appropriate actions for environmental awareness and action
PSO 14:
Demonstrate the capability to participate in community-engaged services/ activities for promoting the well-being of society.
PSO 15:
Demonstrate the ability to identify with or understand the perspective, experiences, or points of view of another individual or group, and to identify and understand other people’s emotions